Dr. Jones Research Lab Website
CONTACT US
ANATOMIC ATLAS FOR THE CANINE LUMBOSACRAL SPINE
Transverse - L6-7 Disc - Zoom
Transverse
Sagittal
Dorsal
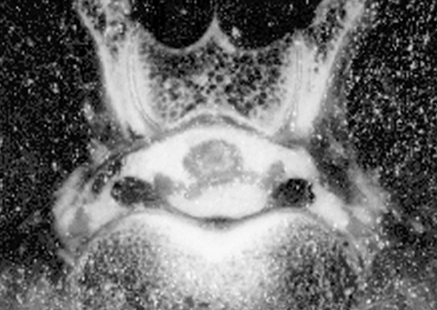
(Jones et al., 1995)
zoom out
1. Thecal sac: Synonym dural sac. Soft tissue opacity CT structure that is enclosed by the dura mater. Tissues inside the thecal sac include the arachnoid membrane, fluid-filled subarachnoid space, nerve roots, and spinal cord. Individual soft tissues inside of the thecal sac are silhouetted in plain CT images and cannot be discriminated.
2. Epidural fat: fat deposits are normally present in the epidural space and appear darker than surrounding nerve tissues on CT images. These fat deposits help provide cushioning and protection of the nerve tissues. In dogs with degenerative lumbosacral disease, loss of visualization of the epidural fat is a sign of nerve tissue compression.
3. Anastomosis: General term that means “communication”. In the lumbosacral spine, the paired branches of the ventral internal vertebral venous plexus have an anastomosis along the dorsal margins of each of the intervertebral discs.
4. L7 nerve roots lead to the cranial gluteal, caudal gluteal, and sciatic peripheral nerves. The cranial and caudal gluteal peripheral nerves innervate the middle gluteal, deep gluteal, and tensor fascia lata muscles, and the superficial gluteal muscles. The sciatic peripheral nerve innervates the biceps femoris, semimembranosus, and semitendinosus muscles, as well as the common peroneal nerve (which innervates the peroneus longus, lateral digital extensor, long digital extensor, and cranial tibial muscles), and the tibial nerve (which innervates the gastrocnemius, popliteus, superficial digital flexor, and deep digital flexor muscles).
5. S1 nerve roots: lead to the cranial gluteal, caudal gluteal, sciatic, and pudendal peripheral nerves. The cranial gluteal peripheral nerve innervates the middle gluteal, deep gluteal, and tensor fascia lata muscles. The caudal gluteal peripheral nerve innervates the superficial gluteal, and middle gluteal muscles.
6. Yellow ligament: Synonyms ligamentum flavum, interarcuate ligament. Loose, thin, elastic sheets between the laminae of adjacent vertebrae. They blend into the joint capsules of the articular processes. In dogs with degenerative lumbosacral stenosis, the yellow ligament at L7-S1 can become thickened or hypertrophied. When this happens, it can cause pain and weakness due to compression of the cauda equina nerve roots.
7. Spinal nerve: Paired, segmental nerves that connect the spinal cord to peripheral structures. In the dog, there are usually 36 pairs. Each spinal nerve consists of 4 components: 1) roots, 2) main trunk, 3) four primary branches, and 4) numerous peripheral branches.
Go to top
2. Epidural fat: fat deposits are normally present in the epidural space and appear darker than surrounding nerve tissues on CT images. These fat deposits help provide cushioning and protection of the nerve tissues. In dogs with degenerative lumbosacral disease, loss of visualization of the epidural fat is a sign of nerve tissue compression.
3. Anastomosis: General term that means “communication”. In the lumbosacral spine, the paired branches of the ventral internal vertebral venous plexus have an anastomosis along the dorsal margins of each of the intervertebral discs.
4. L7 nerve roots lead to the cranial gluteal, caudal gluteal, and sciatic peripheral nerves. The cranial and caudal gluteal peripheral nerves innervate the middle gluteal, deep gluteal, and tensor fascia lata muscles, and the superficial gluteal muscles. The sciatic peripheral nerve innervates the biceps femoris, semimembranosus, and semitendinosus muscles, as well as the common peroneal nerve (which innervates the peroneus longus, lateral digital extensor, long digital extensor, and cranial tibial muscles), and the tibial nerve (which innervates the gastrocnemius, popliteus, superficial digital flexor, and deep digital flexor muscles).
5. S1 nerve roots: lead to the cranial gluteal, caudal gluteal, sciatic, and pudendal peripheral nerves. The cranial gluteal peripheral nerve innervates the middle gluteal, deep gluteal, and tensor fascia lata muscles. The caudal gluteal peripheral nerve innervates the superficial gluteal, and middle gluteal muscles.
6. Yellow ligament: Synonyms ligamentum flavum, interarcuate ligament. Loose, thin, elastic sheets between the laminae of adjacent vertebrae. They blend into the joint capsules of the articular processes. In dogs with degenerative lumbosacral stenosis, the yellow ligament at L7-S1 can become thickened or hypertrophied. When this happens, it can cause pain and weakness due to compression of the cauda equina nerve roots.
7. Spinal nerve: Paired, segmental nerves that connect the spinal cord to peripheral structures. In the dog, there are usually 36 pairs. Each spinal nerve consists of 4 components: 1) roots, 2) main trunk, 3) four primary branches, and 4) numerous peripheral branches.
Go to top
